OUR WORK IS BASED ON SCIENCE
From previous animal studies, we have learned that not only can we slow the rate of aging but in some cases we can reverse it. Today, human trials are starting to show similar outcomes. In fact, we have new ways of measuring aging – biological age, and pace of aging – that is more advanced than previous rate clocks. This new technology is meant to help the masses, not just a certain few which is why we created the Life360 family of programs. So everyone can experience an optimized healthspan aligned with their extended lifespan. Live healthier, longer and better because ‘Longevity is a Lifestyle. Read More
Science-backed Approach
Our team of scientists and doctors are at the forefront of longevity research, and our approach is backed by extensive clinical trials. At Life360, you have access to all the latest advances in age deceleration science so you can stay healthy, vibrant, and youthful for years to come.
Personalized Solutions
Our personalized plans are designed to provide you with tailored guidance in a way that is unique to your needs. We take a data-driven approach to health and longevity, creating customized plans that align with your lifestyle and goals.
Don’t wait to unlock your full potential for a healthier, happier, and more fulfilling life. Join us today and experience what Life360 can offer!
Challenge that Science faces in tackling Longevity
Science faces the challenge of developing comprehensive and integrated solutions for longevity. Most scientific breakthroughs are focused on a single issue, which hinders individuals from creating a holistic approach to anti-aging. More coordination and synthesis of scientific information is needed to help individuals achieve optimal wellness outcomes. The focus of Life360.
By using measurements-based data determined by experts, they can provide targeted recommendations for exercise and physical activity that can help individuals live longer, healthier lives.
Whether you are looking to increase your strength, improve your balance and stability, or simply maintain your overall health and wellness, Life360 has a solution that can meet your needs. Our team of experts can help you create a customized fitness plan that takes into account your current level of fitness, any health concerns you may have, and your long-term goals for your health and well-being. By committing to a tailored exercise regimen and sticking to it, you can unlock the benefits of a longevity lifestyle and increase your chances of living a longer, healthier life. Life360 provides the support, guidance, and expertise needed to make this a reality.
WHY LIFE360?
- We Measure 100+ Biomarkers
- We have holistic interventions across all 5 pillars
- We have medical supervision
- Customized for you and your specific wellness needs.
The Science Behind Aging
Aging is a complex sequence of interconnected processes. Over the past three decades, the field of biomedical research on aging has grown tremendously, leading to the identification of “hallmarks of aging.”
On a cellular level, these processes or “hallmarks” underlie the very machinery that drives the aging of the human body. By better understanding these hallmarks of aging, we can try to slow down or even reverse the aging process and improve overall health and wellbeing.
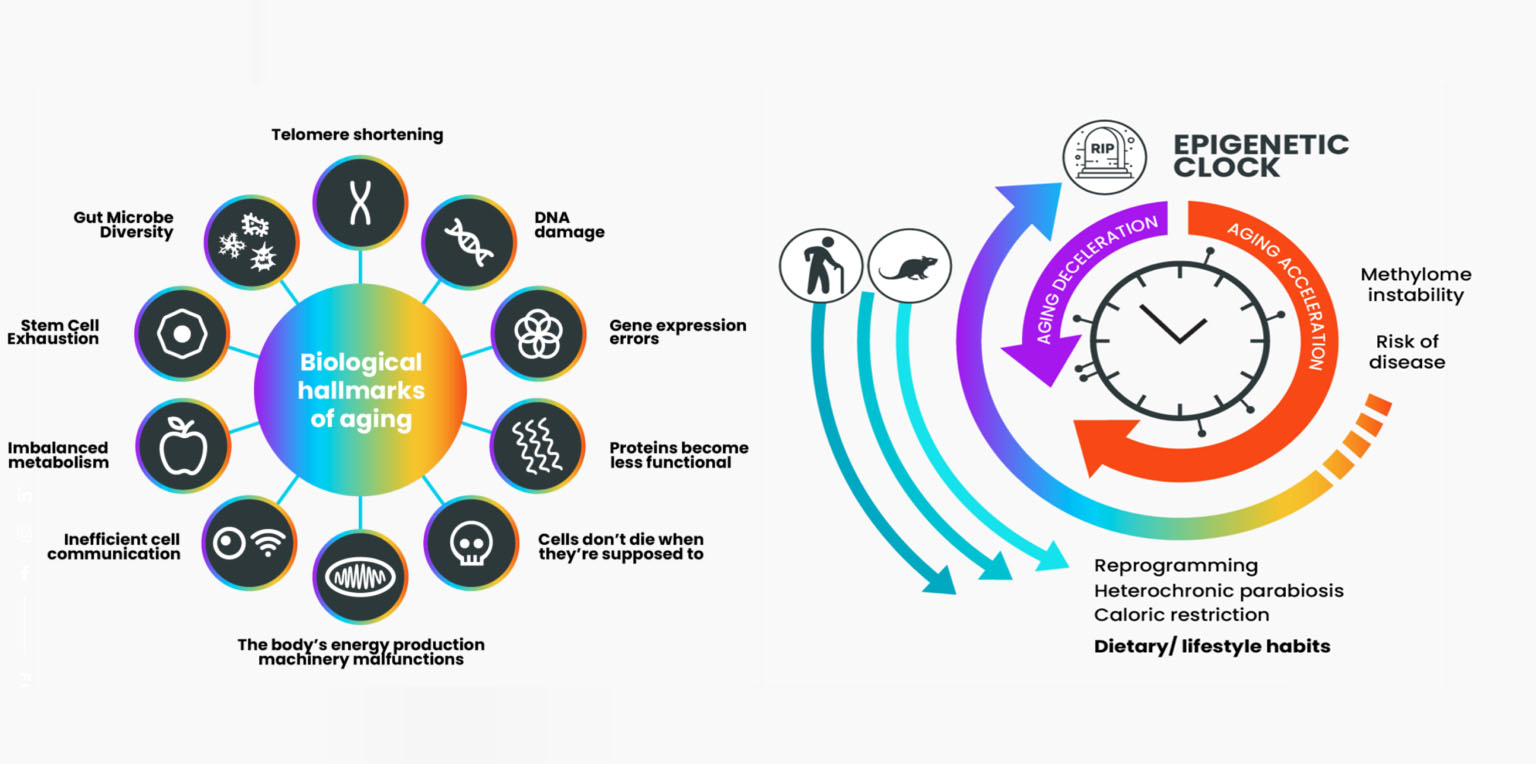
10 Hallmarks Of Aging











The hallmarks of aging are determined mainly by our genetics, but environmental factors can cause or exacerbate them also. Each hallmark contributes to the damage that occurs and accumulates with age and is ultimately responsible for age-associated pathologies. The hallmarks of aging determine the difference between your chronological age and biological age. This is how the aging process has affected your body’s physical and mental functions and appearance, in short, a time-dependent decline.
Genomics Instability
As we age, damage builds up within our cells and DNA, contributing to a phenomenon known as genomic instability. Genomic instability is the process in which our cellular damage accumulates over time and leads to the deterioration of certain elements that our body needs to survive. Our bodies are designed to maintain a specific pattern but as damage builds up, the original design becomes distorted. This damage can lead to unhealthy aging or even premature aging depending on the amount of damage sustained by our cells. As we age we must learn ways to reduce damage and become mindful of activities that may contribute to increased damage over time. Taking this step will allow us to enjoy a healthy life for years.
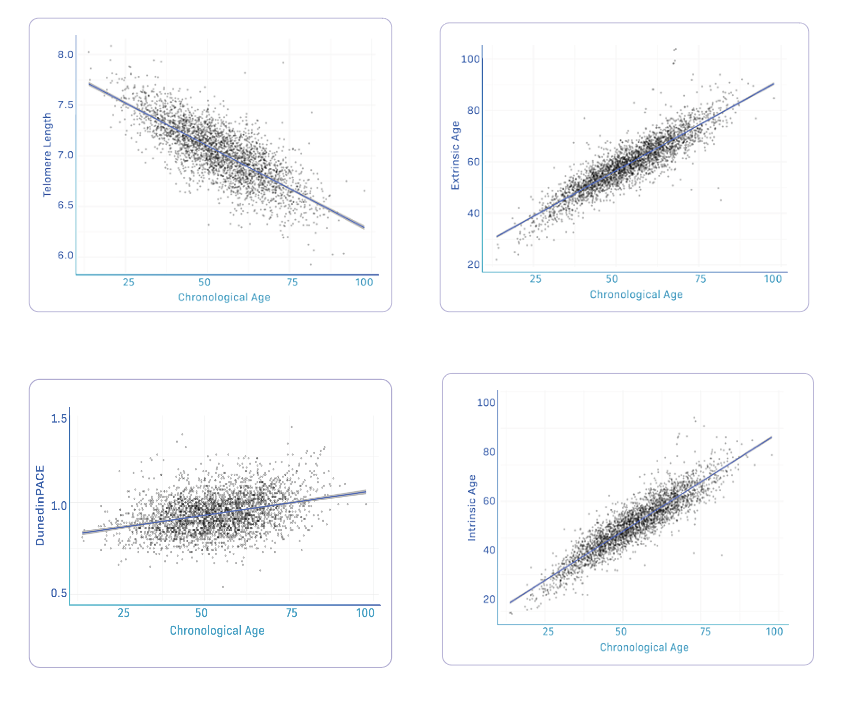
Telomere Attrition
Telomere attrition, damage to the ends of our DNA strands, is thought to be a major contributing factor in the physical process of aging. Cellular damage accumulates over time, causing a multitude of aging effects. This damage can damage our telomeres and trigger their gradual deterioration. As telomeres shorten with age, cells become less and less capable of replication. Studies have shown that as our telomeres wear down due to damage and aging, our longevity decreases as well. Thanks to recent advances in science, it is now possible for people to understand just how damage affects their telomeres and take active steps to prevent or at least slow down the damage accumulating within their cells.
Epigenetic Alterations
The latest science regarding epigenetic alterations and aging reveals damage that accumulates in the DNA of our cells as we get older. Epigenetic damage is thought to contribute significantly to the aging process, and this damage results from a variety of factors, including stress and environmental exposures. Many researchers believe that repairing or preventing this damage could be key to slowing down the signs of aging and living longer. Surprisingly, there is some research which indicates you can alter your epigenetic damage through lifestyle changes, such as eating healthier foods and exercising regularly. It’s remarkable what an impact these modifications can have on cellular health in terms of delaying age-related damage and diseases.
Loss of Proteostasis
Loss of Proteostasis The damage our cells suffer as a result of aging can have serious and long-lasting effects, particularly with regards to proteostasis. Proteostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain balanced levels of proteins required for physiological functioning. As damage to DNA accumulates with age, it interferes with the cell’s ability to produce proteostasis, leading to an increased risk of age-related diseases and declining physical function. The latest research into aging has identified many possible methods for boosting proteostasis in humans, from drugs that target certain proteins and pathways, to dietary changes intended to nourish damaged cellular machinery. These solutions promise improved longevity by helping our bodies fight off damage due to the aging process.
Deregulated Nutrient Sensing
As we age, damage to our cells and DNA accumulate, leading to adverse damage on a cellular level. One such damage is nutrient sensing deregulation, which occurs when the regulation and control of our daily nutrient intake become impaired. This can lead to health complications such as obesity, diabetes and hypertension if left unchecked. Recently, scientists have been researching ways to combat this damage in hopes of slowing down the signs of aging. They believe that by restoring functionality in the nutrient sensing system, it may help to preserve cellular integrity in older individuals and potentially delay the effects of aging at a molecular level. Recent research shows promise to unlock the potential that deregulated nutrient sensing holds for anti-aging treatments.
Mitochondrial dysfunction
As individuals age, damage to the mitochondria of their cells can occur, not only resulting in functional damage but also damage to the DNA of the cells. This damage can then lead to further aging in humans due to issues with cellular damage and toxicity, leading to potential complications with organs and other bodily systems. With recent scientific advancements that are able to measure the damage done by mitochondrial dysfunction, medical professionals are now able to gain a better understanding on where the damage lies and how it is linked with age related issues. As researchers continue making these discoveries, new treatments may be made available for those affected by aging caused by mitochondrial dysfunction.
Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is a process that has long been linked to the aging of the human body, and modern science is unlocking the secrets behind this phenomenon. Cellular damage often accumulates over time, leading to damaged DNA and other damage that can only be repaired if the cell itself undergoes senescence. By doing so, the damage in old cells can be removed from our bodies, helping us to stay healthier and age more gracefully. Not only does new research show how these changes happen in our body as it ages, but scientists are also figuring out ways to help harness cellular senescence in order to prevent damage in people who are growing older. It’s an exciting area of science that promises to provide us with more longevity than ever before.
Stem Cell Exhaustion
As we age, damage builds up in our cellular structure, which is largely caused by the deterioration of DNA over time. This damage makes it increasingly difficult for stem cells to keep up with the body’s needs and leads to what scientists call “stem cell exhaustion.” Recent research is focused on understanding how exactly this process works and how it relates to aging – as well as developing new methods that interact with this natural process of damage accumulation in order to slow down cell damage making us more resilient against aging. One particular area of exploration has been an investigation into how better protecting stem cells would enable our bodies to remain healthy more effectively during old age.
Altered Intercellular communication
As cells age, damage begins to accumulate and their communication pathways break down. This is known as cellular senescence: damage accumulates over time, altering both the phenotype and behavior of the cell. Recent studies have shown that altered intercellular communication between aged cells could be responsible for many features of aging. By understanding how cells communicate and interact with one another, scientists can gain insight into the underlying factors of aging that impede cell function and may even begin to develop treatments to target age-related damage. Science has just begun to uncover the mysteries of how damage affects cell interactions, but already the potential applications are immense; if we can understand what damage occurs at a cellular level when a person ages, we are on the way towards unlocking ways of treating damage caused by aging processes.
Gut Microbe Diversity
We all know that damage accumulates as we age, but did you know that your gut microbe health could play a role in aging? Recent studies have uncovered the intricate details of how our cellular health steadily deteriorates as it ages and how certain strains of gut microbes benefit our longevity. According to one researcher, being able to alter the microbial make-up of an elderly person’s gut “could be a way to prevent damage caused by aging and its associated diseases”. As science is slowly revealing how much promise lies within these tiny organisms found in our bodies, we may experience tremendous advances in treatments for age-related damage.
ANALYTICS & DATA
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
NAD is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It is essential to life because it catalyzes
reactions for more than 400 enzymes, including those involved in the production of
cellular energy (ATP).
NAD plays an essential role in six hallmarks of aging: DNA repair, epigenetic alteration,
loss of proteostasis, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, deregulated nutrient
sensing.
NAD declines with age and lower NAD levels are linked to loss of function and vitality,
and many age-related diseases.
We focus on increasing and maintaining optimal NAD levels, which has been proven to decrease as you age.
Benefits of Optimal NAD
- Increased cellular energy (ATP).
- Improved endurance and strength.
- Improved DNA repair.
- Reduced oxidative stress.
- Greater ability to fight inflammation.
- Improved bone density.
- A number of factors can lower NAD levels.
- Age (NAD declines as we get older).
- Low physical activity.
- Genetic and epigenetic deficiencies (NAD synthesis enzymes).

- Increased cellular energy (ATP).
- Improved endurance and strength.
- Improved DNA repair.
- Reduced oxidative stress.
- Greater ability to fight inflammation.
- Improved bone density.
- A number of factors can lower NAD levels.
- Age (NAD declines as we get older).
- Low physical activity.
- Genetic and epigenetic deficiencies (NAD synthesis enzymes).
- Better prevention of age-related diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, infectious diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, etc. Reduced cellular senescence means better immune health.
Increase your NAD Levels!
Although tryptophan and vitamin B3 (Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide) can be converted into NAD, the efficiency of the process remains to be evaluated by clinical studies.
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is the most efficient NAD precursor to increase NAD level in humans. NR (nicotinamide riboside) may also increase NAD levels in some people
DNA Methylation Test
A variety of lifestyle and environmental factors have been shown to be associated with changes in biological age. Research has shown that biological age is 20% due to genetics, leaving the remaining 80% to be modifiable. We encourage you to adopt healthy lifestyle choices to see what changes work for you to improve biological aging. Abstain from smoking and heavy alcohol consumption. AgeRate research shows that people who do not smoke are, on average, 3-5 years younger biologically than people who smoke regularly. Also, people who do not drink alcoholic beverages tend to live 3-4 years longer than people who drink excessively (15+ drinks per week). Accordingly, an effective way to slow the effects of aging is to practice moderation with these vices. Maintain a healthy weight. AgeRate research finds that people who are leaner tend to have younger biological ages and live longer. A balance of dietary control and regular exercise can help you maintain a healthy weight.
Your Diet Quality Score is based on a study relating DNA methylation changes to diet quality in over 10,000 individuals. Specifically, this study found 26 DNA methylation sites related to diet quality. Notably, some of these diet-associated DNA methylation sites were found to impact genes that played specific roles in our digestive system. To gauge diet quality, this study used two indicators of healthy diet: The Mediterranean Diet Score, which is based on how close your diet resembles that of a traditional Mediterranean diet (emphasizing whole foods, fish intake over red meat, and healthy fats) and the Alternative Healthy Eating Index, which prioritizes healthy dietary habits that protect against age-associated diseases (for example: moderate salt intake). Together, the combination of these two complementary measures of healthy diet lead to a more holistic indicator of diet quality that is not necessarily specific to a single region.
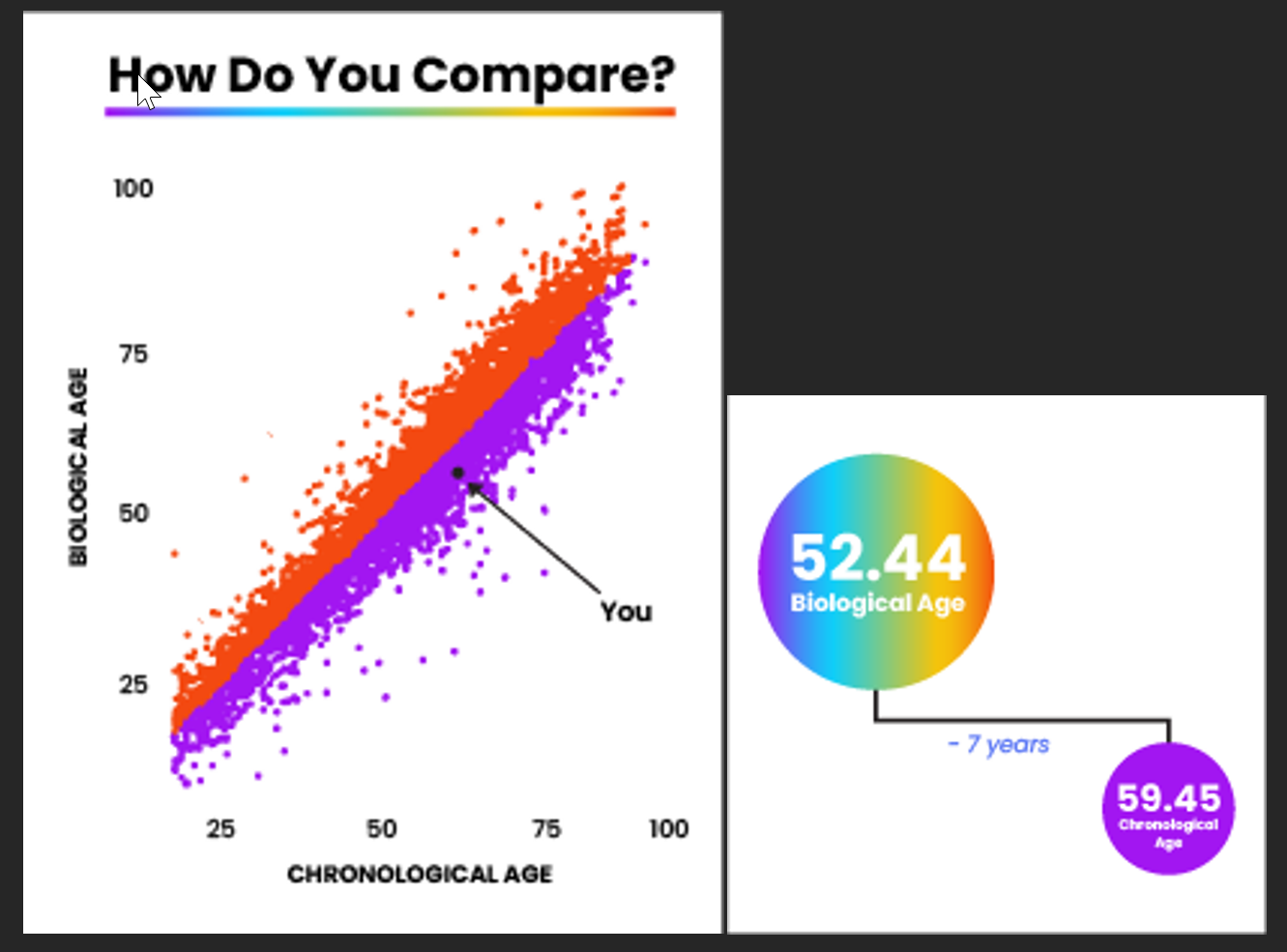
BIOLOGICAL AGING
By measuring your DNA methylation profile and comparing it to a large dataset, we can accurately reveal the age you most represent on a biological level. The AI software program reviews your clinical methylation results from over 900 thousand sites of DNA locations to a baseline subset of data. This baseline reference data has results from people between the ages of 18 to 100 and then rates your individual results across that spectrum. The data continues to evolve and offer predictive measures that correlate to inflammation, disease formation, and genetic tendencies you personally may have. Your biological age has a stronger prediction factor of future health and disease formation than your chronological age
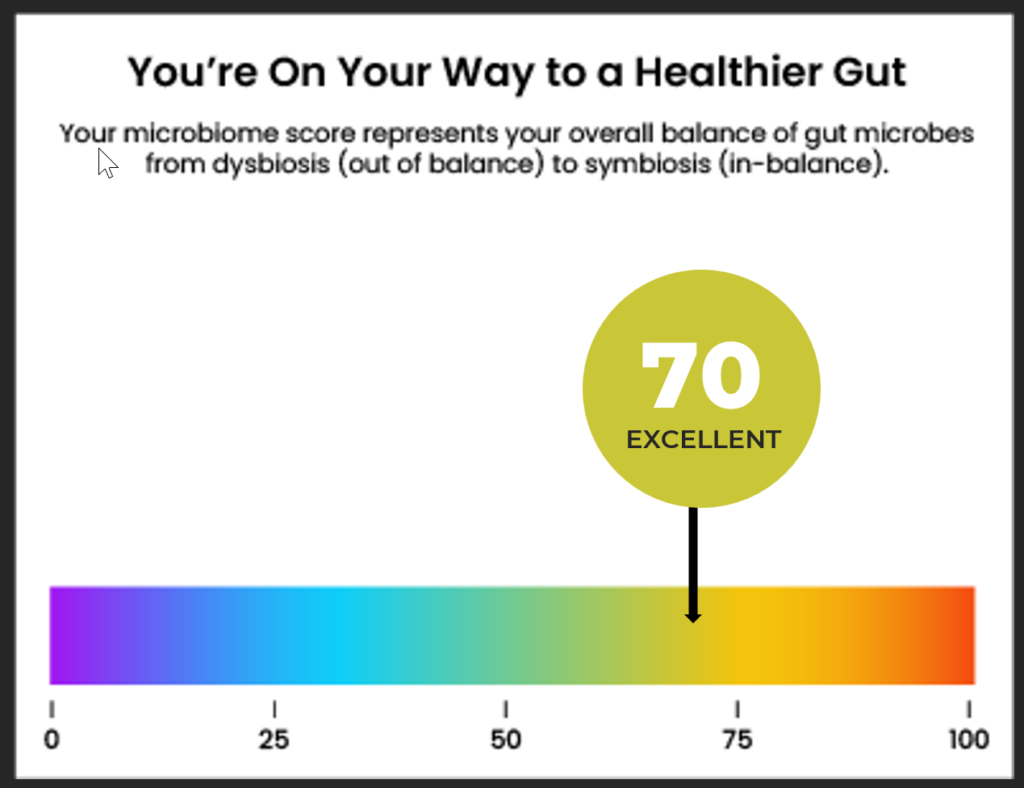
GUT MICROBIOME
There can be over 2000 species of bacterial variations in a single persons’ intestine, which far supersedes the total number of natural human cell variations a human has. There is a correlated relationship between the type of bacteria you have in your intestine and how that affects not only your mental function, but also how well your physical / biological functions perform. As a person ages, the number of bacteria in their intestine and the types therein will change with lifestyle habits including exercise, food intake, alcohol consumption etc. The following is a review of how your gut microbiome compares to the statistical population average.
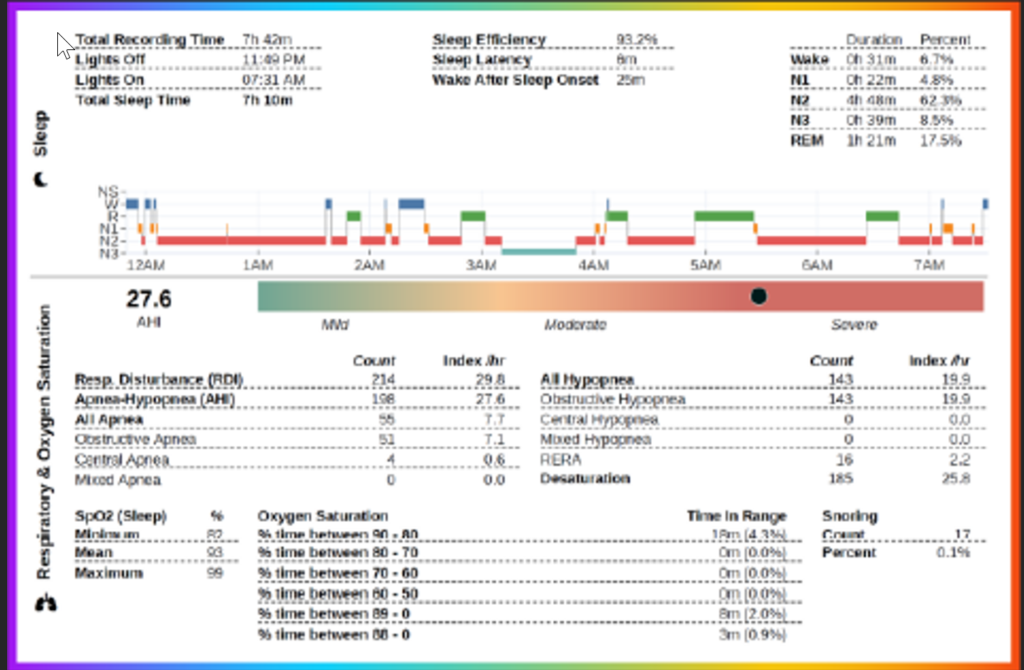
SLEEP EVALUATION
SLEEP EVALUATION Other than having to drink water and eat food, it is arguable that sleep is one of the 3 mainstays of life sustainment but it is often the first to be ignored. The amount of sleep and the quality of sleep dictates how well you function both mentally and physically. Sleep hygiene habits and evaluation for sleep disorders is one of the key tenants to staying young and healthy.
SEROLOGICAL MARKERS
Your blood can reveal a tremendous amount of data on how specific organs are functioning in addition to whether you carry markers for inflammation that could be causing premature aging. Your body is a system of cellular processes that jointly work in concert to function at an optimal level. When certain processes are not functioning, it causes chaos and disruption within your whole body. These biomarkers will help us identify specific areas to focus on as we improve your cellular biology.
| Test Name | Description | Test Date | Serum Level |
| Glycated serum protein | 2-3 week indicator of average blood glucose | ||
| Vitamin D | Vitamin D direct measurement | ||
| High sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP) | Measurement of inflammation | ||
| Low density lipoprotein (LDL) | Bad cholesterol | ||
| Albumin | Liver / kidney health measurement | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) | Liver injury and function | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | Liver / bone function test | ||
| High density lipoprotein (HDL) | Good cholesterol | ||
| Creatinine (serum) | Kidney function test | ||
| Triglyceride | Measurement of fat correlated to diet habits and heart or artery health | ||
| Creatine Kinase | Test for function of skeletal, heart, or brain muscle tissue | ||
| Uric acid | Cellular health / kidney function | ||
| Cortisol (saliva) | Measurement of stress levels and adrenal gland function |
PHYSICAL SUSTAINMENT
Maintenance of physical strength and mobility is a core factor in determining how quickly your body deteriorates as you age. If you maintain physical activity, your body and its effect on your mind have been scientifically proven to extend life and create a healthy lifespan. Measurement of your physical ability, is a good indicator of where you are currently and how it could be improved.
SUMMARY
Based on the tests included on this report, we assign a weighted average based on the criteria measured to develop a wellness index. This current index will be reevaluated after our 24 week LIVE100 program in order to determine the gains you can attain on overall health and biological age sustainment or reversal at the end of the program.
SEROLOGICAL MARKERS
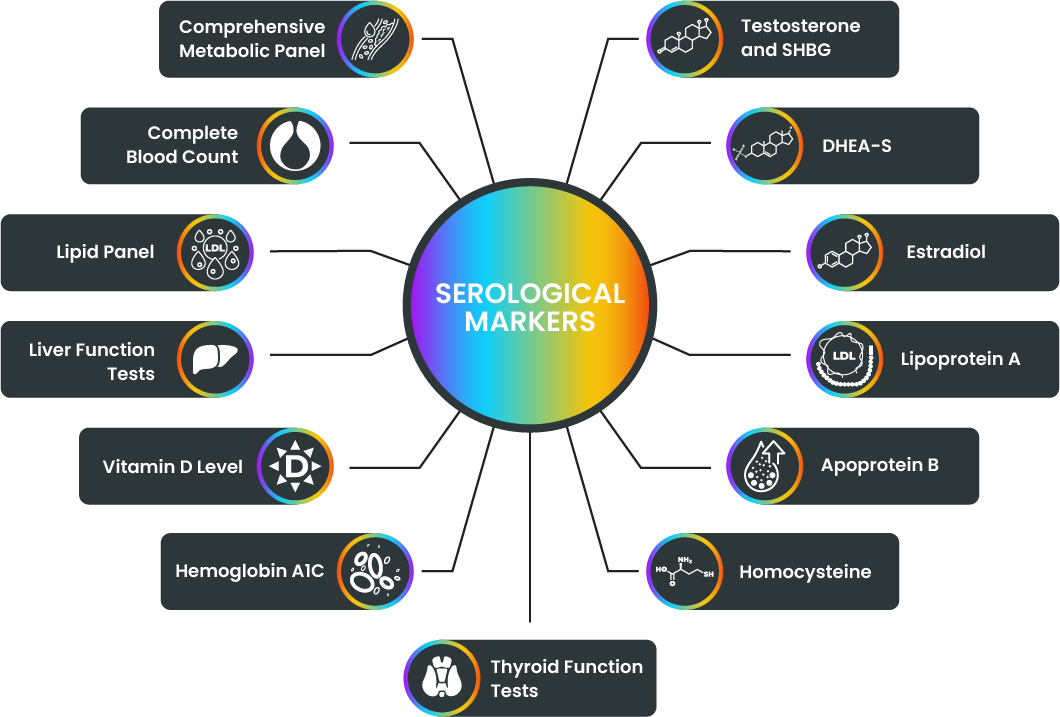
Evaluates organ health by measuring electrolytes, glucose, kidney and liver function markers, and protein levels. Provides insight into overall metabolic function and helps identify imbalances affecting wellness.
Assesses blood cell levels, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Detects anemia, infection, and inflammation, providing an overview of general health status and immune system function.
Measures cholesterol levels, including LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. Assesses cardiovascular health, identifies risks for heart disease, and guides dietary and lifestyle interventions to promote wellness.
Measures liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins to assess liver health and function. Helps identify liver damage, inflammation, or impaired detoxification, which can impact overall wellness.
Measures circulating vitamin D levels. Adequate levels are crucial for bone health, immune function, and overall wellness. Deficiencies may contribute to various health issues.
Assesses average blood sugar control over several months. Evaluates diabetes risk and monitors glucose regulation, highlighting the importance of metabolic health and disease prevention.
Measures thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4) to assess thyroid gland function. Thyroid health affects metabolism, energy levels, and overall wellness.
Measures testosterone levels and sex hormone-binding globulin. Evaluates hormone balance and supports optimal vitality, muscle mass, mood, and sexual health.
Measures DHEA-S levels, an adrenal hormone. Provides insight into adrenal function, stress response, and overall hormone balance.
Measures estradiol levels, a primary female sex hormone. Evaluates hormonal balance and supports reproductive health, bone density, and overall wellness.
Lipoprotein(a) is a specific type of cholesterol particle. Elevated levels of lipoprotein(a) are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. It can contribute to the buildup of plaques in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and potential health complications.
Apoprotein B is a protein that is a component of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol). Measuring apoprotein B levels provides additional information beyond the standard lipid panel measurements. Elevated levels of apoprotein B indicate an increased number of LDL particles, which can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and raise the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Measures homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to heart disease and other health conditions. High levels can indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular issues and may highlight the need for interventions to support heart health.
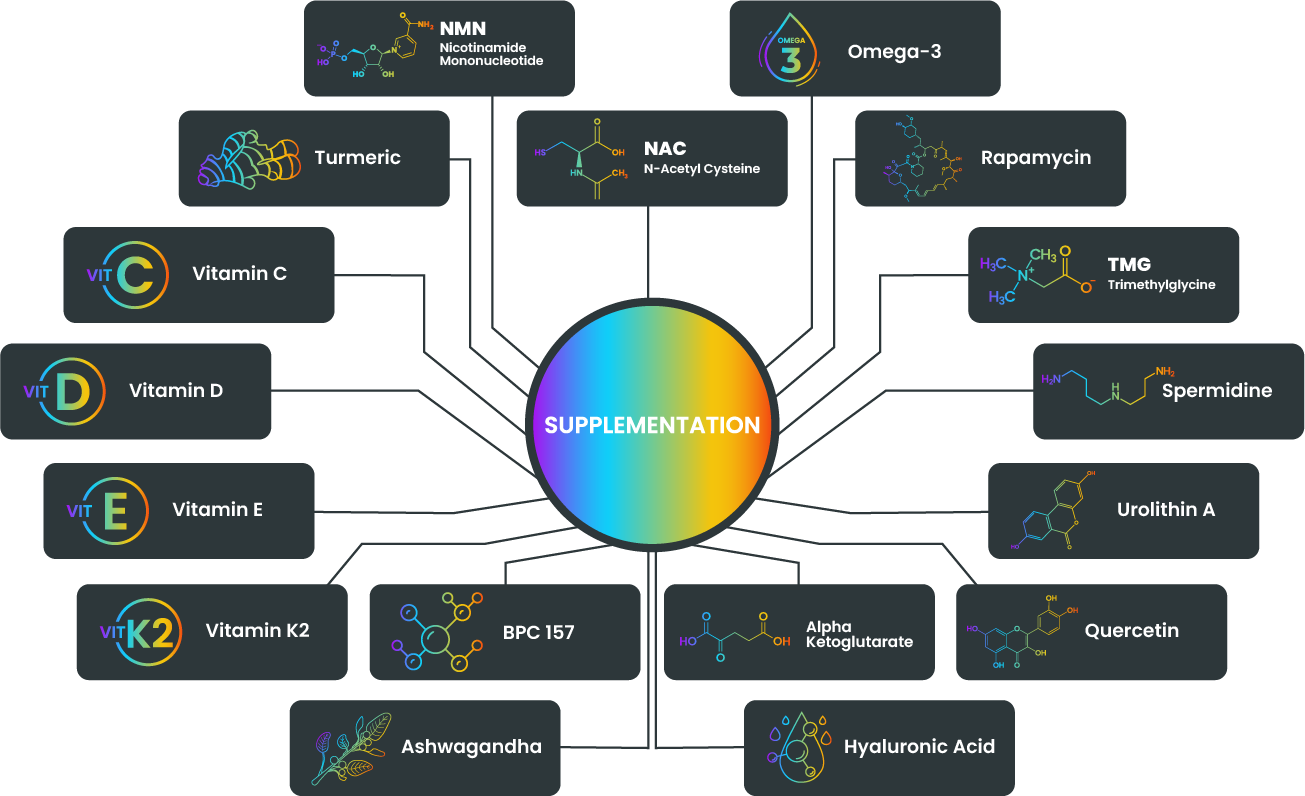
SUPPLEMENTATION
– Mitochondrial dysfunction: NMN supports mitochondrial function and energy production, addressing age-related decline in mitochondrial health.
– Cellular senescence: NMN may help reduce the accumulation of senescent cells, promoting cellular rejuvenation.
– Inflammation: Turmeric exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
– Oxidative stress: Turmeric acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress.
– DNA damage: Vitamin C helps protect DNA from damage caused by oxidative stress.
– Cellular senescence: Vitamin C may help delay cellular senescence and promote healthy cell function.
– Immune system decline: Vitamin D supports immune function, addressing age-related decline in immune response.
– Bone health: Vitamin D helps maintain bone density and reduces the risk of age-related bone loss.
– Oxidative stress: Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
– Skin aging: Vitamin E supports skin health, reducing the impact of environmental factors on skin aging.
– Bone health: Vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in calcium metabolism, supporting bone health and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
– Stress response: Ashwagandha helps modulate the stress response, supporting resilience and reducing the impact of chronic stress on aging.
– Cognitive decline: Ashwagandha may have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing age-related cognitive decline.
– Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
– Heart health: Omega-3 supports cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of age-related heart disease.
– Cellular senescence: Rapamycin inhibits the mTOR pathway, which plays a role in cellular senescence, potentially slowing down the aging process.
– Oxidative stress: TMG acts as a methyl donor, supporting the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress.
– Inflammation: TMG has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
– Autophagy: Spermidine induces autophagy, promoting cellular recycling and rejuvenation.
– Cellular senescence: Spermidine may help inhibit cellular senescence and support healthy cell function.
– Mitochondrial dysfunction: Urolithin A activates mitophagy, improving mitochondrial function and addressing age-related mitochondrial dysfunction.
– Inflammation: Quercetin exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
– Oxidative stress: Quercetin acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
– Tissue regeneration: Hyaluronic acid plays a role in tissue repair and regeneration, contributing to overall tissue health.
– Skin aging: Hyaluronic acid supports skin hydration and elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
– Metabolic dysregulation: Alpha ketoglutarate supports cellular metabolism and energy production, addressing age-related metabolic dysregulation.
– Stem cell exhaustion: Alpha ketoglutarate can support stem cell function, potentially delaying stem cell exhaustion.
– Oxidative stress: NAC boosts glutathione levels, reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage.
– Inflammation: NAC exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, modulating the immune response and reducing chronic inflammation.
– Tissue repair: BPC 157 promotes tissue repair and healing, supporting recovery from injuries and age-related damage.
– Inflammation: BPC 157 reduces inflammation and supports gut and neurological health.